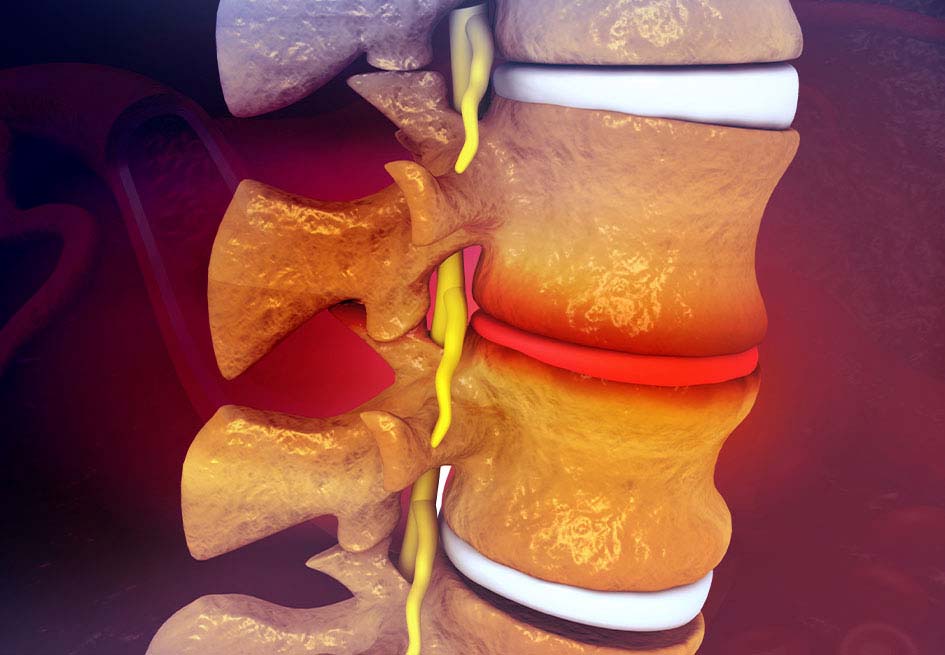
In this article we are going to talk about dorsal disc herniations or thoracic disc herniations .
The dorsal column corresponds to the mid-upper area of the back and, although thoracic disc herniations are not very common, sometimes they can cause serious symptoms since the diameter of the spine at this height is smaller, so The risk of spinal cord injury cannot be ruled out if you have a dorsal disc herniation.
Thoracic disc herniations are very rare , they are only 0.5% of disc herniations, they are most common between the ages of 50 and 80 and affect both sexes equally. Most dorsal disc herniations occur at the lowest levels of the dorsal column, the most affected discs are D11 and D12 and in 25% of cases there may be a history of trauma.
Table of Contents
Symptoms of dorsal hernias
Mid-upper back pain
Pain is the main symptom caused by a dorsal hernia. Usually it is a pain centered on the middle area of the back at the height at which we have the hernia.
Neuropathic pain
If the herniated thoracic disc compresses the nerve roots, neuropathic pain can occur. Neuropathic pain is characterized by being like an intense burning , it is a pain that does not change with movements. In the case of the dorsal column, the pain would radiate through the rib cage to the sternum.
myelopathy
When a herniated thoracic disc damages the spinal cord, myelopathy can occur. If this occurs, symptoms such as loss of sensitivity in the legs and the area of the chest below the hernia may appear . In addition to sensitivity, leg strength is also affected. Many times myelopathy is accompanied by lack of sphincter control .
How is a dorsal hernia diagnosed?
The imaging test that best helps us diagnose this type of herniated discs is magnetic resonance imaging. In an MRI we will see where the hernia is located and if it compresses the spinal cord (1).
Another important test for a correct diagnosis of a dorsal disc herniation is the CT scan. In many cases the hernia may be calcified. Since the hernia is calcified, it is hard and can determine how to approach a possible surgical treatment.
Treatment of dorsal hernias
Conservative treatment
As always, unless the symptoms caused by the hernia are serious, we must begin treatment conservatively. Analgesics, anti-inflammatories and muscle relaxants are the basis of conservative treatment. In cases where we also have neuropathic pain, medications such as pregabalin or gabapentin can be associated.
Once the most acute phase of pain is over, it is important to exercise and improve muscle tone .
Dorsal disc herniation surgery
Unfortunately, on some occasions when the pain does not subside and the neurological symptoms are significant, it is necessary to operate to remove the hernia .
At this point it is important to decide where the herniated disc is going to be addressed. Access to the dorsal column can be carried out via a posterior, posterolateral or anterior route.
Posterior approach
It consists of accessing the spinal canal by performing a lamientomy, this access is almost not used, the dorsal spinal cord cannot be moved to access the hernia that is in its anterior part, so it is often not possible to remove the hernia and spinal injuries can occur.
Posterolateral approach
In this case we will access the disc from the back, usually, instead of doing a laminectomy we will remove the part of the rib where it joins the vertebra and we will reach the disc by dissecting the lateral part of the vertebra.
With the development of new technologies, today access can be made through the hole through which the nerve root exits using an endoscopy. Through a 1 cm access, dilating the muscles we would introduce a chamber inside the spine through which we can pass the different instruments that would allow us to remove the herniated disc.
Previous approach
With this approach we will reach the disk from its anterior part. As we have talked about, the spinal cord cannot be mobilized due to the risk of neurological injury and sometimes to reach a dorsal disc herniation this is the only option.
To carry out this approach we will make an incision in the lateral part of the thorax and we will separate or remove part of the rib. Once the muscles have been dissected we will have to deflate a lung to be able to reach the disc from its anterior part and thus perform the discectomy.
For this technique we can use a thoracoscope to be less invasive.
Conclusions about dorsal hernias
Thoracic disc herniations, as we have talked about, are very rare, but sometimes they can cause serious symptoms and even cause spinal injuries. That is why it is important to identify the symptoms of a dorsal disc herniation so that you can go to your doctor and he or she can establish the most appropriate treatment.